(Click the card to view its details)
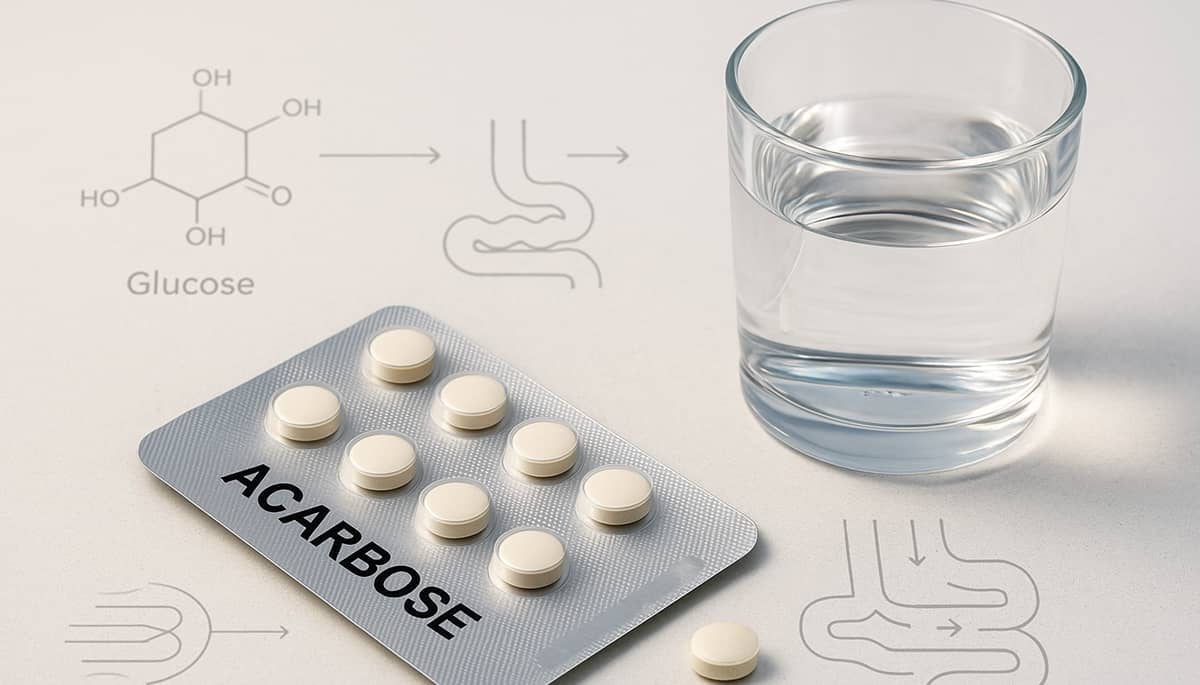
Acarbose
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Low
Acarbose is an α-glucosidase inhibitor used in the treatment of type 2 diabetes, which, in addition to lowering postprandial glucose spikes, supports gut and cardiovascular health. This drug shows moderate benefits in reducing body weight and improving the lipid profile and blood pressure. Additionally, through its influence on gut microbiota and short-chain fatty acid production, it may support intestinal barrier function and reduce inflammation.

Aerobic training
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Negligible
Aerobic training is regular physical activity of moderate or high intensity, including running, walking, swimming, or cycling. It leads to reduced risk of heart disease, improved mood, and decreased body fat mass. It is a universal tool for prevention and supporting health in virtually every age group.

AGE Reader (Diagnoptics)
Level:Advanced
Usefulness:Medium
AGE Reader by Diagnoptics provides a non-invasive evaluation of Advanced Glycation End-products (AGEs) by measuring skin autofluorescence. AGEs are harmful compounds formed through the non-enzymatic reaction between sugars and proteins or lipids, and they accumulate with age and metabolic stress. High AGE levels are associated with accelerated aging, diabetes complications, cardiovascular diseases, and oxidative stress. This test offers insights into cumulative metabolic and oxidative damage, serving as a proxy for long-term health risk and biological aging.

Aged garlic (kyolic)
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Negligible
Aged garlic extract (Aged Garlic Extract, Kyolic, AGE) is a standardized extract with a proven beneficial effect on heart, vascular, and metabolic health. Numerous clinical studies indicate AGE’s effectiveness in lowering blood pressure, improving lipid profiles, and supporting gut microbiota. The supplement is well tolerated and can be a safe component of prevention and support therapy for cardiovascular diseases.

Air pollution
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
Air pollution is one of the most important environmental factors reducing both lifespan and quality of life. Both particulate matter (PM2.5, PM10) and nitrogen oxides or ozone cause a range of serious cardiovascular diseases, respiratory diseases, and cognitive impairments. Even short-term exposure worsens health, while long-term exposure significantly increases the risk of heart attack, stroke, lung cancer, and dementia.

Alcohol
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
Alcohol consumption—regardless of dose—is associated with an increased risk of numerous diseases, shortened lifespan, and deterioration of both physical and mental health. Alcohol is toxic to body cells, damages the liver, brain, and heart, and promotes the development of cancers and metabolic disorders.
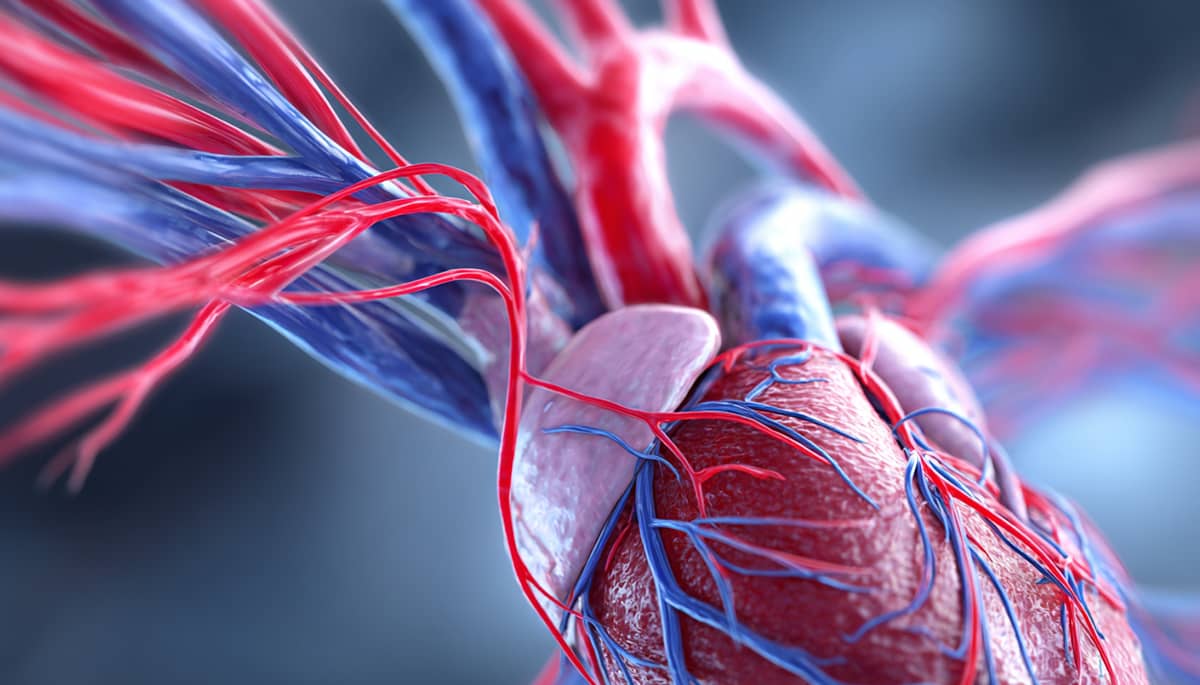
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring – 24h (SOMNOmedics)
Level:Intermediate
Usefulness:Medium
Ambulatory Blood Pressure Monitoring (ABPM) using the SOMNOmedics SOMNOtouch NIBP device provides continuous 24-hour measurement of systolic and diastolic blood pressure during normal daily activities and sleep. This method allows for precise assessment of blood pressure variability, detection of masked or nocturnal hypertension, and evaluation of dipping patterns that are strongly linked with cardiovascular risk. Unlike office-based measurements, ABPM offers a real-world view of blood pressure behavior throughout the day and night, supporting more accurate diagnosis and therapy optimization.
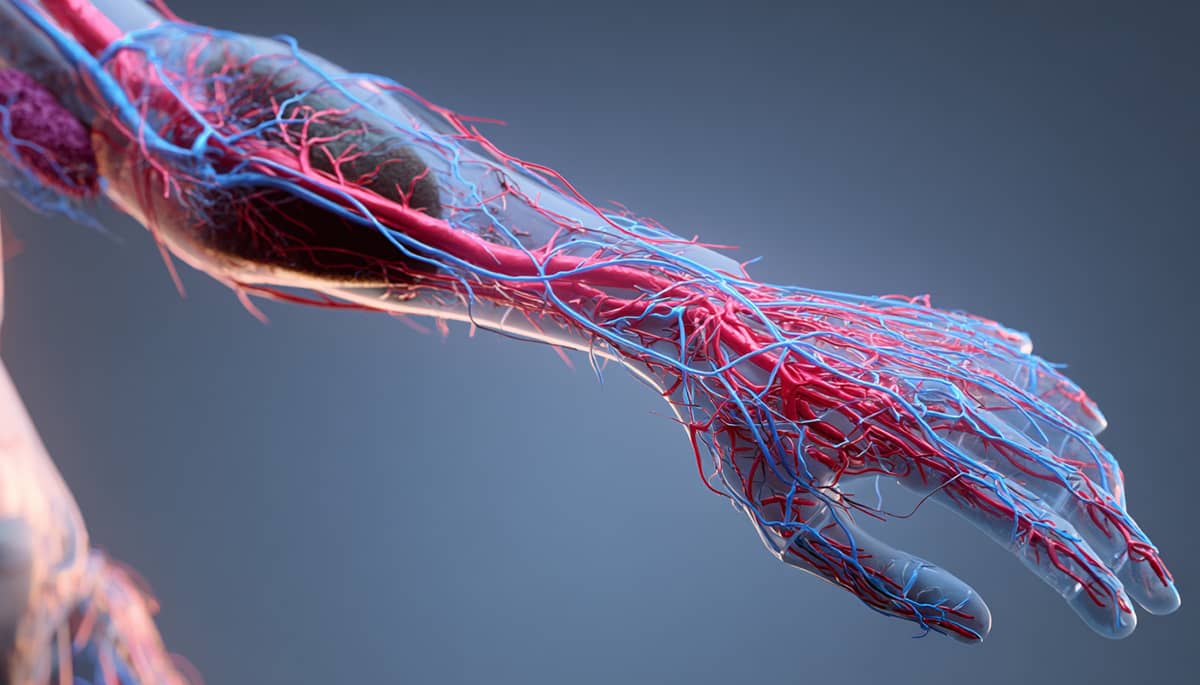
Ankle-Brachial Index (MESI)
Level:Intermediate
Usefulness:Medium
The Ankle-Brachial Index (ABI) is a simple, non-invasive test that compares blood pressure in the ankle with that in the arm. It helps detect peripheral artery disease (PAD), a condition where narrowed arteries reduce blood flow to the limbs. Early detection of PAD is important because it may indicate widespread atherosclerosis, which increases the risk of heart attack and stroke. This test is particularly valuable for individuals over 50, smokers, diabetics, and those with high cardiovascular risk.

Apple cider vinegar
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Low
Apple cider vinegar is a popular natural supplement that may support weight loss, improve lipid profile, and help regulate blood glucose levels. It is particularly beneficial for people who are overweight, obese, or have metabolic disorders, supporting a healthy lifestyle.

Appropriate hydration
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Negligible
Maintaining adequate hydration helps to preserve optimal performance during exercise and daily activities, reduces feelings of fatigue, and supports efficient brain and cardiovascular function.
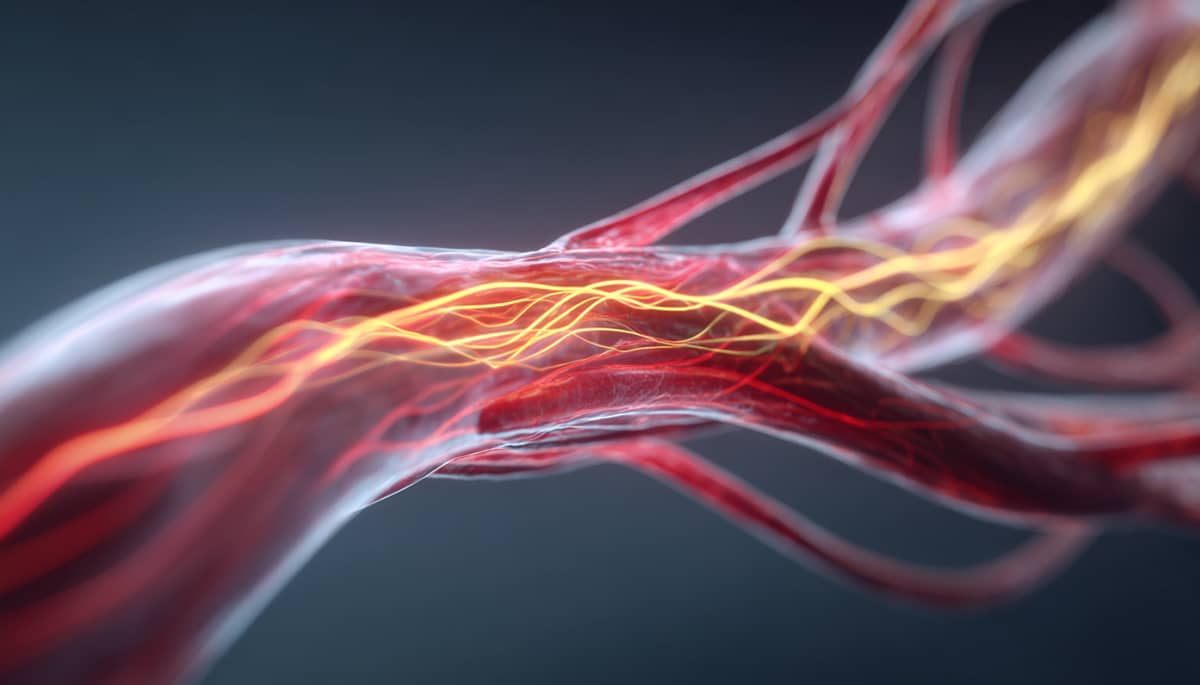
Arterial Stiffness & Central Blood Pressure (SphygmoCor)
Level:Intermediate
Usefulness:Medium
This non-invasive test evaluates the elasticity of your arterial system and the central blood pressure (the pressure in the aorta close to the heart). As arteries stiffen with age or disease, they reflect more pressure back toward the heart, which increases cardiac workload and elevates long-term risk for hypertension, heart attack, stroke, and kidney disease. The SphygmoCor Pulse Wave Analysis system uses waveform technology to measure: - Central systolic and diastolic pressure - Augmentation Index (AIx) - Pulse Wave Velocity (PWV) These metrics are often more predictive of cardiovascular risk than traditional arm-cuff blood pressure readings.

Ashwagandha
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Low
Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera) is an adaptogen with documented effects in reducing stress, anxiety, and improving sleep quality and cognitive functions. Supplementation with ashwagandha supports body recovery, increases resilience to stressors, and improves mood and mental well-being. Numerous clinical studies and meta-analyses confirm its effectiveness and good safety profile.

Balance training
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Negligible
Balance training supports the musculoskeletal system by improving stability and functionality in daily activities. Regular exercises reduce the risk of falls, correct muscle imbalances, and increase movement efficiency. Benefits include better mobility, reduced pain in patients with joint diseases, and improved athletic performance.
Blood Age Test (Deep Longevity)
Level:Advanced
Usefulness:Low
The Blood Age Test (Deep Longevity) is an AI-driven assessment that estimates your biological age based on standard blood biomarkers. Unlike conventional lab tests that measure individual parameters, this model analyzes the collective patterns and deviations within your blood panel to predict how fast your body is aging relative to your chronological age. Using a proprietary deep-learning algorithm trained on thousands of blood samples, the test interprets subtle biological signals of cellular wear and systemic health decline. It provides a single, interpretable score — your "Blood Age" — and compares it to your real age, showing whether you are aging faster or slower than average.

Blueberries
Impact:High
Evidence:Strong
Blueberries are nutrient-dense, polyphenol-rich fruits renowned for their wide-ranging effects on cardiovascular, cognitive, and metabolic health. Their deep-blue pigments are rich in anthocyanins — potent antioxidants and signaling molecules that support vascular elasticity, glucose regulation, and neuroprotection. Regular consumption has been linked to reduced risk of type 2 diabetes, improved endothelial function, better memory performance, and slower cognitive decline. Blueberries also influence gut microbiota composition, contributing to improved immune and metabolic balance. These cumulative effects make them one of the most evidence-backed functional foods for promoting healthy aging and longevity.
Body composition analysis (Lunar iDXA)
Level:Intermediate
Usefulness:High
Dual-energy X-ray absorptiometry (DXA) with the GE Lunar iDXA scanner is a highly precise diagnostic used to assess body composition — including total and regional fat mass, lean tissue, and bone mineral density. It’s considered the gold standard in both research and clinical settings for evaluating body composition and bone health. Compared to BIA or skinfold methods, DXA provides much more accurate and detailed measurements. It allows for early detection of visceral fat accumulation, osteoporosis risk, or muscle loss — making it invaluable for longevity, performance, and metabolic health tracking.
Body composition analysis (Tanita)
Level:Beginner
Usefulness:High
Bioelectrical impedance analysis (BIA) using Tanita devices offers a fast, non-invasive way to evaluate your body composition — including body fat percentage, muscle mass, visceral fat rating, and more. This information helps establish a baseline, monitor progress, and guide interventions for fat loss, muscle gain, or metabolic health. As one of the most accessible diagnostics, BIA supports longevity by revealing how your body is adapting to nutrition, training, and lifestyle. While not as precise as DXA, it’s ideal for consistent self-tracking and making data-informed health decisions from the very beginning of your journey.

Body fat percentage
Impact:High
Body fat percentage (BF%) reflects the balance between fat and lean tissue and is a fundamental determinant of health, performance, and aging. Unlike body weight or BMI, BF% offers direct insight into metabolic function, disease risk, and physical capacity. Monitoring and maintaining BF% within optimal ranges supports healthy longevity and resilience.

Body scan 3D (Styku)
Level:Intermediate
Usefulness:Medium
The 3D body scan by Styku offers a fast, non-invasive way to capture your full body shape, posture, and circumferential measurements. Using infrared imaging and a rotating platform, it creates a 360° digital avatar — allowing users to track body changes in fat distribution, waist-to-hip ratio, and shape over time. While not as precise as DXA or Tanita for body composition, it adds a unique visual dimension. It helps enhance accountability and motivation, offering clear visualizations of transformation that go beyond the scale.
Bone Mineral Density (BMD)
Impact:High
BMD quantifies mineral content per bone area (g/cm²), primarily via DXA, and strongly predicts fracture risk and broader health outcomes. It differs from T-score and Z-score, which contextualize a person’s BMD against reference populations.
Botox in vascular and sexual function therapy
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Preliminary
Risk:Elevated
Botox (botulinum toxin) administered locally into the corpora cavernosa or pelvic muscles can improve blood flow and reduce excessive spasms, resulting in better erectile function in men and quality of sexual life in women with OAB, vaginismus, or vulvodynia. The therapy is well tolerated, and clinical studies show significant improvements in IIEF, EHS, and FSFI scales. Further, larger, and long-term studies are needed to confirm the durability of effects and safety of the intervention.

Broccoli
Impact:High
Evidence:Strong
Broccoli is a nutrient-dense cruciferous vegetable recognized for its powerful combination of vitamins, minerals, fiber, and bioactive compounds such as sulforaphane and indole-3-carbinol. These compounds activate detoxification pathways, reduce inflammation, and support healthy metabolism. Regular broccoli intake has been associated with lower all-cause mortality and reduced risks of cancer and cardiovascular disease. Beyond disease prevention, broccoli contributes to gut and metabolic health, promoting longevity through mechanisms linked to oxidative stress reduction and cellular resilience.

Caloric restriction (~10%)
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Low
Caloric restriction involves a moderate reduction in calorie intake (about 20–25%) while maintaining complete nutrition. It shows beneficial effects on metabolic and cardiovascular risk factors such as blood pressure, lipid profile, and body composition. Additionally, it may support cellular repair processes and reduce inflammation, promoting a longer healthy lifespan.
Cancer Markers Panel
Level:Advanced
Usefulness:Medium
Cancer marker panels assess specific proteins, antigens, or molecules that may be elevated in the blood during cancer development or progression. Common examples include PSA (prostate), CA-125 (ovarian), CEA (colon), AFP (liver), and CA 19-9 (pancreatic). While these markers are invaluable in oncology for tracking recurrence or therapy response, they are not precise screening tools for asymptomatic individuals. Elevated levels can occur in non-cancerous conditions, making contextual interpretation essential.

Chronic dehydration
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:Elevated
Chronic dehydration means a prolonged water deficiency in the body, resulting from insufficient fluid intake or excessive loss. This condition often develops silently, and its effects may manifest gradually, leading to an increased risk of serious health disorders. Particularly at risk are the elderly, children, and individuals who perform intense physical work or stay in high temperatures.

Chronic emotion suppression
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:Elevated
Chronic emotional suppression is the habitual restraint from expressing and experiencing emotions, both negative and positive. This emotion regulation strategy, especially common in Western cultures, is strongly linked to poorer mental health and social relationships, as well as increased risk of somatic diseases, particularly cardiovascular diseases.

Chronic lack of rest and relaxation
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
Chronic lack of rest and inability to relax include prolonged sleep deficiency, lack of regular breaks at work, chronic stress, and inability to use relaxation techniques. This lifestyle leads to lasting disturbances in bodily function, increased risk of depression, heart disease, weakened immunity, and reduced overall well-being.

Chronic micronutrient deficiency
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
Chronic deficiency of micronutrients and vitamins is a state in which the body does not receive or absorb sufficient amounts of key nutrients for an extended period. This results in impaired functioning of many body systems, increased risk of chronic diseases, and reduced quality and length of life.

Chronic psychological stress
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
Chronic psychological stress is one of the most significant negative factors affecting health and lifespan. Prolonged exposure to stress leads to mood disorders, impaired cognitive functions, and accelerates the development of many chronic diseases, including those of the heart and brain. Stress affects every stage of life, with its effects accumulating with age and worsening overall quality of life.

Coffee
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Low
Coffee is a popular beverage containing caffeine, chlorogenic acids, and polyphenols, which support alertness, memory, and executive functions, as well as protect hepatocytes and blood vessels. Moderate consumption (2–5 cups per day) is associated with reduced risk of neurodegenerative diseases, cirrhosis, and liver cancer, as well as a decreased risk of cardiovascular diseases and stroke. Additionally, it exhibits antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects, supporting the body's overall homeostasis.

Cold plunge
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Elevated
Regular cold exposure, such as winter swimming or cold baths, supports metabolic, immune, and mental health, bringing benefits such as improved insulin sensitivity, enhanced immunity, and stress reduction. While weight loss effects are moderate, the intervention promotes improvements in body composition and well-being. In adapted individuals, better resistance to infections and increased levels of positive emotions are also observed.

Collagen
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Negligible
Collagen is a structural protein essential for the condition of joints, skin, tendons, bones, as well as hair and nails. Supplementation with hydrolyzed collagen shows well-documented beneficial effects on joint health (pain reduction, improved mobility), skin hydration and elasticity, and tissue regeneration after physical exertion. Regular collagen use may support overall fitness, reduce injury risk, and improve external appearance.

Collagen peptides (oral)
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Negligible
Oral collagen peptides are widely used supplements aimed at improving skin condition, supporting joint health, and aiding muscle recovery. Numerous studies confirm their beneficial impact on skin hydration and elasticity, joint pain reduction, increased bone mineral density, and faster recovery after physical exertion. Collagen supplementation is especially recommended for older adults, physically active individuals, and those with skin or joint issues.
Complete Blood Count (CBC)
Level:Beginner
Usefulness:High
A Complete Blood Count (CBC) is a routine diagnostic test that evaluates the levels of various cells in your blood, including red blood cells, white blood cells, and platelets. It helps assess general health and detect a wide range of disorders, such as infections, anemia, and hematological abnormalities. This test is widely used as a first-line health screening, often included in annual checkups or pre-treatment evaluations. It offers a quick, cost-effective snapshot of systemic health, immune activity, and potential red flags requiring further investigation.

Comprehensive Functional Assessment (ddRobotec)
Level:Intermediate
Usefulness:Medium
ddrobotec® is a Swiss diagnostic and training system that analyzes neuromuscular function, balance, and coordination of the lower limbs. It combines robotics, force sensors, and AI-driven software to measure the body’s responses to dynamic loads. This allows for precise assessment of strength, reaction speed, and the cooperation between the nervous system and muscles. It is used both in elite sports and rehabilitation, helping to monitor progress and the efficiency of the musculoskeletal system.
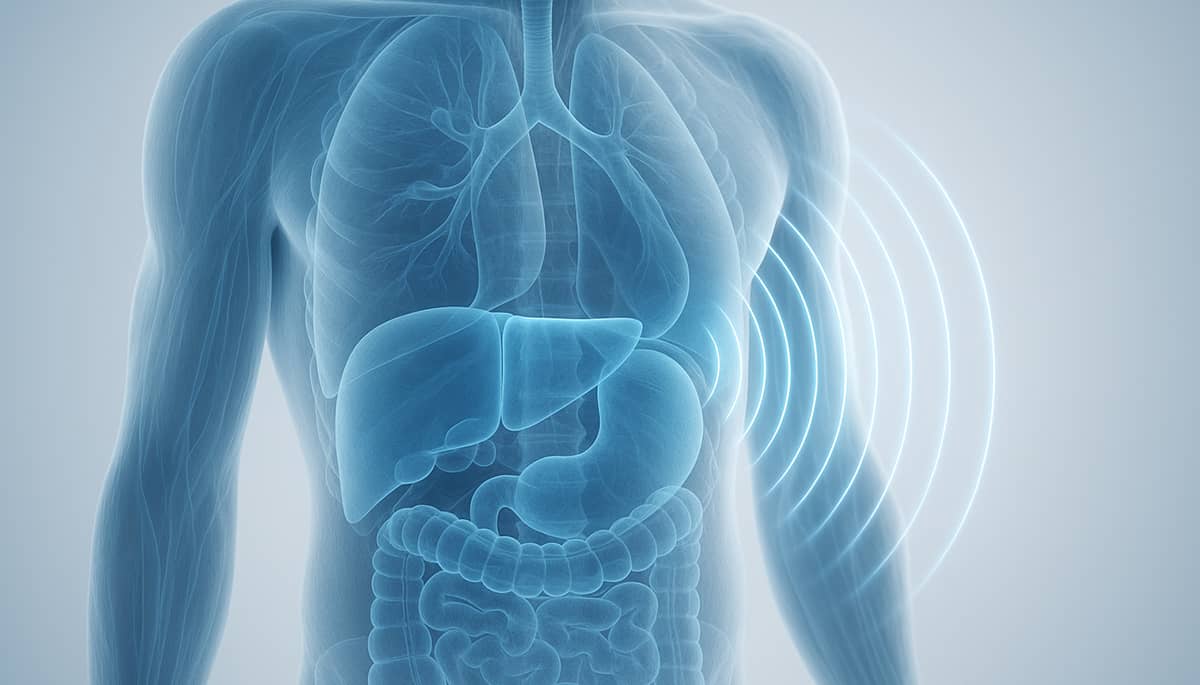
Comprehensive Ultrasound Screening
Level:Beginner
Usefulness:High
Comprehensive Ultrasound Screening is a non-invasive imaging procedure designed to evaluate key internal organs and detect potential abnormalities before symptoms arise. This preventive examination uses high-resolution ultrasonography to visualize the structure and function of major organs, including the abdomen, thyroid, and reproductive organs. The test provides valuable insights into the health of the liver, kidneys, pancreas, gallbladder, spleen, thyroid gland, and testicles, among others. It helps identify early structural changes such as cysts, nodules, or benign and malignant tumors, supporting proactive medical intervention and lifestyle adjustments. As part of routine preventive care, this screening contributes to early cancer detection, organ health assessment, and monitoring of long-term physiological stability.

Consistent sleep and wake time (incl. weekends)
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Negligible
Regular sleep and wake times are one of the most effective and simplest interventions to support mental health, overall well-being, and body recovery. Maintaining a consistent circadian rhythm improves sleep quality, reduces the risk of depression, anxiety, and mood disorders, and supports repair processes in the body and brain. This strategy is effective across all age groups – including children, adolescents, adults, and the elderly.

Continuous Glucose Monitoring (FreeStyle LibreLink)
Level:Intermediate
Usefulness:High
Continuous Glucose Monitoring (CGM) with the FreeStyle LibreLink system by Abbott allows real-time tracking of glucose levels using a small wearable sensor placed on the upper arm. The sensor measures interstitial glucose every few minutes, providing a continuous 24-hour profile of glycemic fluctuations and responses to meals, exercise, sleep, and stress. The accompanying LibreLink app and LibreView platform visualize glucose trends, daily patterns, and variability metrics such as Time in Range (TIR), Glucose Management Indicator (GMI), and coefficient of variation (CV). These insights help optimize diet, activity, and recovery strategies — whether for diabetes management or longevity-focused metabolic optimization. CGM empowers users to understand their body’s glycemic responses, improve insulin sensitivity, and maintain stable energy throughout the day without frequent finger-prick tests.
Cortisol Diurnal Profile (Biovis)
Level:Intermediate
Usefulness:Medium
The Cortisol Diurnal Profile (Biovis) is a salivary test that evaluates the natural fluctuations of cortisol across the day — typically measured at morning, midday, and evening timepoints. This curve reveals how well the body's stress system (HPA axis) is functioning, and whether chronic stress, burnout risk, or circadian disruption may be present. Cortisol should normally peak in the morning and gradually taper off throughout the day. Deviations from this pattern — such as low morning levels or elevated evening cortisol — can indicate impaired stress resilience, fatigue, or dysregulation of the circadian rhythm.
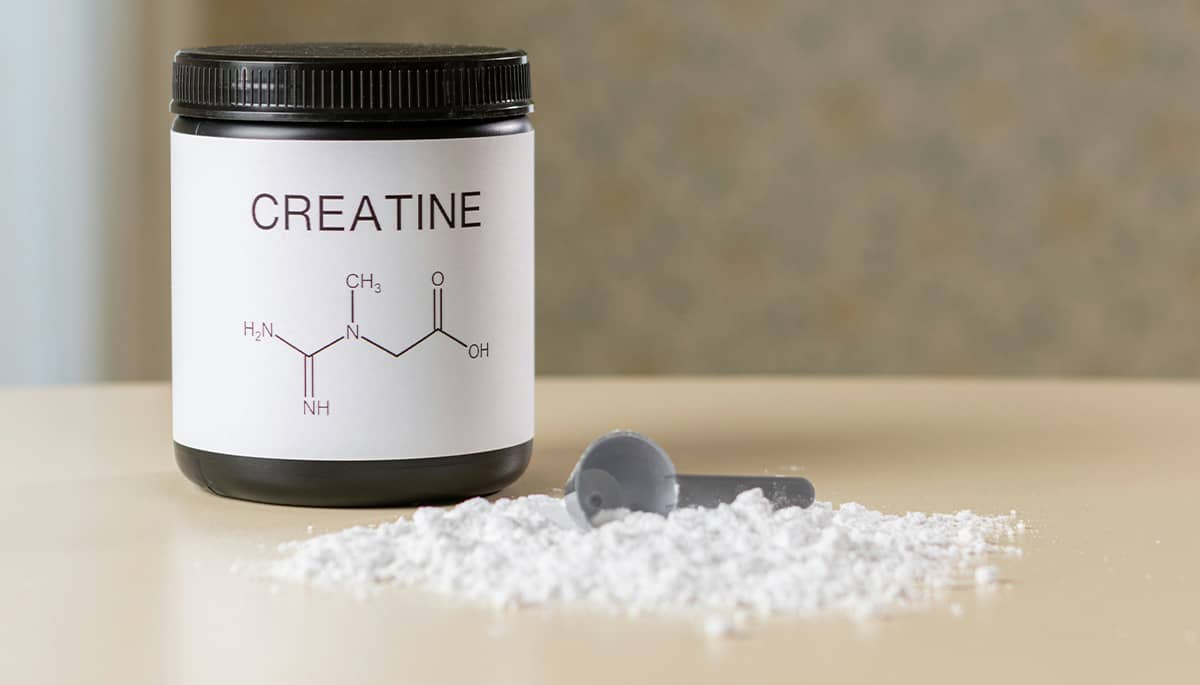

Creatine
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Negligible
Creatine is a well-researched supplement that supports increases in lean body mass and muscle strength. Regular supplementation, especially when combined with resistance training, accelerates recovery and reduces muscle damage. It may also provide cognitive benefits and support bone health.

Cryotherapy
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Low
Cryotherapy is a therapeutic method that uses cold to reduce pain, fatigue, and inflammation, particularly effective in acute injuries, postoperative rehabilitation, and certain chronic conditions. It helps restore range of motion, improves well-being, and supports physical functioning.

Darkness in the bedroom
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Negligible
Darkness in the bedroom significantly improves sleep quality in both adults and children. Limiting exposure to light at night leads to faster sleep onset, fewer awakenings, and deeper recovery, as confirmed by numerous clinical and observational studies.

DunedinPACE (TruDiagnostic)
Level:Advanced
Usefulness:Low
DunedinPACE (Pace of Aging Computed from the Epigenome) is an advanced epigenetic biomarker developed by the Dunedin Study research team and implemented by TruDiagnostic. Unlike traditional biological age clocks, which estimate cumulative age, DunedinPACE measures the *speed* at which your body is aging right now. It calculates the rate of physiological decline across multiple biological systems by analyzing methylation patterns in DNA. A score of 1.0 means you are aging at the average rate of one biological year per chronological year. A value below 1.0 suggests slowed aging, while values above 1.0 indicate accelerated aging. This test has gained prominence in longevity research as one of the most robust and reproducible measures of biological aging, providing unique insight into how lifestyle and interventions influence long-term health trajectories.

Early time-restricted feeding (etrf)
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Low
Early time-restricted feeding (eTRF) involves consuming all meals in the first half of the day, typically within a 6–8-hour window. Studies confirm that this strategy improves insulin sensitivity, regulates glucose levels, lowers blood pressure, and has a positive effect on lipid profile and gut microbiota health. eTRF may support metabolic health regardless of weight loss.

Eating in a hurry
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Good
Harm:Elevated
Fast eating, typical of the modern lifestyle, leads to impaired satiety and promotes overeating. Numerous studies indicate that eating in a hurry increases the risk of metabolic syndrome, abdominal obesity, hypertension, and disturbances in lipid and carbohydrate metabolism. Regularly practicing fast eating contributes to worsening health parameters and the development of lifestyle diseases.

Eating right before bed
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Good
Harm:Elevated
Eating right before bedtime, especially large and high-calorie meals, may negatively affect metabolism, sleep quality, and the body's regenerative processes. Late-night eating is associated with an increased risk of insulin resistance, obesity, and sleep disorders, which consequently impacts health and longevity. At the same time, small, nutritious snacks consumed before bedtime can support muscle recovery, particularly in physically active individuals, provided that heavy and sweet foods are avoided in the evening.

Electrocardiogram
Level:Basic
Usefulness:Medium
An electrocardiogram (ECG or EKG) is a fast, non-invasive test that records the electrical signals in your heart. It’s used to identify irregular heart rhythms, structural abnormalities, and signs of past or impending heart problems. It’s often the first-line test for evaluating cardiac symptoms such as chest pain, palpitations, dizziness, or fatigue — but it can also be part of a proactive cardiovascular health assessment.

Epigenetic Health Report (Muhdo)
Level:Advanced
Usefulness:Low
The Comprehensive Epigenetic Health Report (Muhdo) analyzes DNA methylation patterns to evaluate how lifestyle and environmental factors influence gene expression and biological aging. Unlike purely genetic tests, this report reflects how external factors — diet, sleep, exercise, and stress — have shaped the current functional state of your genome. The test estimates overall biological age, the biological age of selected organ systems (vision, hearing, memory), and evaluates inflammatory and anti-inflammatory gene activity patterns. These metrics provide a snapshot of cellular health and recovery potential. Although informative, epigenetic age tests should be interpreted cautiously. Results may vary due to sample quality and current physiological conditions (e.g., recent illness, stress, or inflammation), and they provide a momentary reflection rather than a long-term baseline.
Epitalon and thymulin (injectable peptides)
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Preliminary
Risk:Elevated
Epitalon and thymulin are peptides administered in the form of injections, which exhibit potential neuroprotective, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory properties. Preclinical studies suggest their beneficial effects on nerve cells, immune system balance, and slowing the development of certain cancers. Both peptides are the subject of intensive research, but currently, there is a lack of conclusive clinical evidence confirming their effectiveness in humans.
Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR)
Level:Beginner
Usefulness:Medium
The Erythrocyte Sedimentation Rate (ESR) measures how quickly red blood cells settle at the bottom of a test tube. A faster-than-normal rate may indicate inflammation in the body caused by infection, autoimmune disease, or chronic conditions. While nonspecific, ESR remains a valuable and inexpensive tool for detecting inflammatory activity and monitoring disease progression over time. It is often used alongside C-reactive protein (CRP) for a more complete picture of inflammation.

Evening blue light exposure
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Good
Harm:Elevated
Evening exposure to blue light disrupts the natural circadian rhythm, reduces sleep quality and duration, and increases the risk of mood disorders and depressive symptoms. Prolonged exposure can lead to deteriorating mental health, impaired cognitive function, and a risk of neurodegeneration, especially in adolescents and sensitive individuals.

Evening calming ritual (30–60 min)
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Negligible
Evening calming rituals, including meditation, relaxation techniques, and mindfulness, show proven effects in reducing fatigue and supporting the body's recovery. Regular practice of these techniques promotes better sleep quality, improved well-being, and emotional balance, which translates into higher energy levels the next day.

Excess high glycemic food intake
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Good
Harm:Elevated
Consuming large amounts of high glycemic index (GI) foods leads to rapid increases in blood glucose and insulin levels. A long-term diet rich in high GI products promotes the development of insulin resistance, type 2 diabetes, obesity, and increases the risk of cardiovascular diseases. Particularly harmful is the regular consumption of highly processed carbohydrates, such as white bread, sweets, or sugary drinks.

Excessive caffeine intake
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Good
Harm:Elevated
Chronic and high consumption of coffee or caffeine is associated with reduced sleep quality and duration, as well as increased risk of anxiety, stress, and depressive symptoms, especially in sensitive individuals. These effects intensify with dosage and the timing of caffeine intake, particularly in the afternoon and evening hours.

Excessive porn consumption
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Good
Harm:Elevated
Excessive consumption of pornographic content is a phenomenon increasingly observed in societies with widespread internet access. Scientific studies indicate that regular and intensive use of pornography may lead to negative psychological consequences such as an increased risk of depression, anxiety, reduced self-esteem, and problematic compulsive behaviors. This phenomenon particularly concerns young people and individuals with increased psychological vulnerability.

Excessive red meat consumption
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
Excessive consumption of red meat, both processed and unprocessed, is clearly associated with an increased risk of many serious chronic diseases. Regular intake of large amounts of this type of meat leads to metabolic disorders, vascular wall damage, inflammation, and increased risk of gastrointestinal cancers. Harmful effects are observed even with moderate exceedance of recommended amounts, especially in populations following a Western dietary pattern.

Excessive salt intake
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
Excessive consumption of table salt is one of the most important and best-documented environmental factors increasing the risk of hypertension, stroke, heart attack, chronic kidney disease, and dementia. Salt present in the Western diet exceeds WHO recommendations by several times, leading to a significant increase in morbidity and premature death.

Excessive social media use
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:Elevated
Excessive use of social media is widespread and shows a clear negative impact on mental health and sleep. Numerous studies indicate that people who frequently and compulsively use social media are more likely to experience symptoms of depression, anxiety, stress, and deteriorating well-being. These effects are particularly visible among adolescents and young adults.

Excessive sugar intake
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
Excessive sugar consumption, especially in the form of added sugars and sugar-sweetened beverages, is a widespread public health issue. Numerous studies show that excess sugar leads to the development of insulin resistance, obesity, fatty liver, type 2 diabetes, and cardiovascular diseases. The harmful effect of sugar is particularly evident in the case of regular consumption of sweetened beverages, which increases the risk of serious metabolic complications and shortens lifespan.

Excessive trans fat intake
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
Excessive consumption of trans fats is one of the key risk factors for many chronic metabolic and cardiovascular diseases. Its presence in the diet contributes to an increased risk of heart disease, type 2 diabetes, non-alcoholic fatty liver disease, and many other metabolic disorders, which translates to a shortened lifespan and reduced quality of life.

Excessive uv exposure
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
Excessive exposure to UV radiation is considered one of the most significant threats to the health of the skin and eyes. It causes DNA damage, accelerates aging processes, weakens the immune system of the skin, and increases the risk of skin cancers and serious eye diseases such as cataracts or pterygium. Prolonged exposure without proper protection carries serious health consequences, which can be effectively minimized by using protective measures.

Exercise Metabolic and Performance Analysis (PNOE)
Level:Beginner
Usefulness:High
The Exercise Metabolic and Performance Analysis (PNOE) is a gold-standard metabolic test that evaluates how your body produces and utilizes energy during physical exertion. Using breath-by-breath analysis of oxygen (VO₂) and carbon dioxide (VCO₂), it provides a detailed profile of aerobic and anaerobic metabolism, cardiovascular efficiency, and fat-burning capacity. The test identifies your unique ventilatory thresholds (VT1 and VT2), maximum oxygen uptake (VO₂peak), and FatMax — the exercise intensity at which fat oxidation is maximized. These metrics are essential for tailoring endurance training, improving performance, and optimizing longevity-focused exercise routines. The PNOE system is used globally by sports scientists, physicians, and longevity experts to design personalized metabolic and cardiovascular health programs.

Extreme diet monotony
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Good
Harm:Elevated
A monotonous diet, consisting of long-term consumption of the same foods, results in a decrease in the diversity of nutrients and gut microbiota. The lack of dietary variety weakens immune mechanisms, promotes inflammation, and increases the risk of metabolic disorders and gastrointestinal diseases. Maintaining such a diet over a longer period can lead to chronic health problems, even though negative effects may develop slowly and depend on other lifestyle factors.

Fast food
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
Regular consumption of fast food is one of the main factors promoting the development of obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, and metabolic disorders. Fast foods are characterized by high caloric content, large amounts of saturated and trans fats, salt, and sugars, which quickly lead to deterioration of health parameters, especially in individuals with predispositions or lack of physical activity.

Fermented vegetables
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Negligible
Fermented vegetables, thanks to the presence of probiotics, bioactive metabolites, and nutrients, have a beneficial effect on health by supporting gut microbiota, the immune system, and improving the metabolic profile. Regular consumption of these products may help reduce inflammation, improve gut health, and support the immune system in fighting infections and diseases.

Fisetin
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Preliminary
Risk:Low
Fisetin, a natural flavonoid present in fruits and vegetables, exhibits broad health-promoting effects, particularly in the context of metabolism, cancer protection, and neuroprotection. In preclinical studies, fisetin improves glucose and lipid metabolism, reduces inflammation, protects the liver, supports the fight against obesity, and shows anti-inflammatory and antioxidant effects. Additionally, fisetin shows potential in cancer prevention by affecting cancer cell growth, inducing apoptosis, and regulating signaling pathways associated with cancer development.

Flexibility training (stretching)
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Negligible
Flexibility training, i.e., regular stretching, is an effective method for improving joint range of motion and reducing stiffness in muscles and periarticular tissues. This leads to better physical performance, reduced risk of injuries, and supports muscle recovery after exertion.

Functional Strength & Performance Test
Level:Beginner
Usefulness:High
This functional test evaluates key aspects of physical performance — including strength, endurance, power, and mobility. It combines practical field exercises such as grip strength, pull-ups, long jump, and Airbike endurance. It is one of the **most important diagnostics for healthspan and longevity**, as it measures real-world capacity — not theoretical potential. Regular performance testing enables precise tracking of progress in core longevity domains like muscle mass, strength, and physical independence.
Gene therapy (follistatin)
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Preliminary
Risk:High
Gene therapy using follistatin delivers the gene encoding this protein to muscles, leading to a significant increase in muscle mass and strength as well as metabolic benefits. Preclinical studies have also demonstrated a reduction in inflammation and improved glycemic control. This approach may represent an innovative strategy for treating muscular dystrophies, type 2 diabetes, and obesity.

Genetic Health Profile (Muhdo)
Level:Advanced
Usefulness:Medium
The Comprehensive Genetic Health Profile (Muhdo) is an advanced DNA test that analyzes hundreds of single nucleotide polymorphisms (SNPs) to uncover individual genetic predispositions influencing physical performance, nutrition, vitamin metabolism, recovery capacity, mental resilience, and long-term health risks. This test helps users understand how their genes may affect traits such as muscle power and endurance, carbohydrate and fat metabolism, inflammatory response, sleep quality, stress resilience, and susceptibility to injury. Unlike clinical diagnostics, it does not measure current biomarker levels but provides insights into inherent tendencies — guiding more effective personalization of training, supplementation, and lifestyle strategies. The Muhdo platform integrates genetic science with lifestyle coaching, offering a user-friendly report that translates complex genomic data into clear, actionable recommendations for health optimization.

Ghk-cu and skin peptides (topical)
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Preliminary
Risk:Negligible
GHK-Cu and its derivatives are copper peptides with documented anti-aging and regenerative effects. They stimulate the synthesis of collagen and glycosaminoglycans, which improves skin firmness and elasticity. They also show antioxidant and anti-inflammatory properties, supporting protection against oxidative stress.

GlycanAge Test (GlycanAge Ltd.)
Level:Advanced
Usefulness:Low
The GlycanAge Test (GlycanAge Ltd.) measures biological age through the analysis of immunoglobulin G (IgG) N-glycosylation patterns. By quantifying 29 glycan structures from a blood sample, the test assesses how chronic inflammation and immune system aging — known as inflammaging — affect your overall biological age. Glycans regulate immune function by modifying the inflammatory potential of antibodies. The test provides several glycan-based indexes (Shield, Youth, Mature, Median, Lifestyle) that together describe the balance between pro- and anti-inflammatory immune activity. A higher “GlycanAge” than your chronological age may suggest elevated systemic inflammation or accelerated immune aging, while a lower score indicates better immune regulation and slower aging. Although scientifically robust, this test is not diagnostic and should be interpreted in context with lifestyle factors, hormonal balance, and other biological age markers.
Glycemic Panel (Glucose + HbA1c)
Level:Beginner
Usefulness:High
The glycemic panel includes fasting blood glucose and Hemoglobin A1c (HbA1c) — two complementary markers that provide both short-term and long-term insights into how your body regulates blood sugar. It is a critical diagnostic for detecting prediabetes, diabetes, insulin resistance, and glucose dysregulation that may go unnoticed in early stages.

Green tea
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Negligible
Green tea is a popular beverage with a proven beneficial effect on cardiovascular health and metabolism. Regular consumption helps lower LDL cholesterol levels, improve lipid profile, regulate blood pressure, and supports weight management. There is also preliminary evidence of a protective effect in the prevention of certain cancers, especially with high consumption.

Heart Rate Variability Monitoring (Firstbeat)
Level:Intermediate
Usefulness:Medium
This test uses a wearable device from Firstbeat to continuously monitor heart rate variability (HRV), providing insight into autonomic nervous system activity, stress levels, recovery capacity, and sleep quality over several days. The data can help users understand how their body responds to different stressors, physical activity, and recovery protocols, offering a dynamic picture of overall resilience and well-being.

High polyphenol olive oil
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Negligible
High-polyphenol olive oil is a natural dietary supplement with proven antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, and immunomodulatory effects. Regular consumption supports heart health, improves lipid profile and glycemic control, and strengthens the immune system, making it a valuable component in the prevention of chronic diseases.

High-intensity interval training (hiit)
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Low
High-Intensity Interval Training (HIIT) is an effective and time-efficient method for improving health across multiple domains. It positively affects the cardiovascular, metabolic, and mental health systems. Through intense, short training sessions, HIIT promotes fat reduction, enhances insulin sensitivity, boosts aerobic capacity, and reduces symptoms of depression and anxiety.
High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein (hs-CRP)
Level:Intermediate
Usefulness:High
High-Sensitivity C-Reactive Protein (hs-CRP) is a blood test that detects low levels of systemic inflammation. Unlike standard CRP tests used in acute infections, hs-CRP measures subtler elevations that may reflect chronic, low-grade inflammation. Chronic inflammation plays a key role in the development of heart disease, metabolic dysfunction, cognitive decline, and other age-related conditions. Measuring hs-CRP can provide insight into hidden risk factors and guide lifestyle or protocol adjustments.

Home Sleep Apnea Test (WatchPAT)
Level:Intermediate
Usefulness:Medium
The WatchPAT Home Sleep Apnea Test is a clinically validated, wearable diagnostic tool used to assess sleep structure, breathing irregularities, and oxygen saturation. Unlike traditional in-lab polysomnography, this test is performed at home over a single night using a small wrist-mounted device with sensors that monitor pulse rate, oxygen levels, and peripheral arterial tone (PAT). The test provides data on total sleep time, sleep stages, apnea–hypopnea index (AHI), oxygen desaturation index (ODI), and average heart rate during sleep. It helps detect potential sleep apnea and related respiratory disturbances that affect recovery, cognitive function, and cardiovascular health. While the WatchPAT test offers valuable clinical insight, it represents only a one-night snapshot. Continuous monitoring via long-term wearables such as WHOOP, Oura Ring, or Apple Watch can provide a more accurate picture of habitual sleep quality and recovery dynamics.
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (hbot)
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Elevated
Hyperbaric oxygen therapy (HBOT) involves breathing pure oxygen under increased pressure in a special chamber. It is used as an adjunctive treatment in many clinical conditions, such as chronic wounds, sports injuries, osteonecrosis, radiotherapy complications, and selected neurological disorders. It supports regenerative processes, reduces inflammation, and improves microcirculation, which can lead to faster recovery and improved quality of life.
IgG4 Foodscreen (Biovis)
Level:Intermediate
Usefulness:Medium
The IgG4 Foodscreen test analyzes the presence of specific IgG4 antibodies against a wide range of common dietary proteins. Elevated IgG4 levels may indicate delayed food sensitivities — a distinct phenomenon from immediate allergic reactions (IgE-mediated). This test is often used to guide elimination diets for individuals with chronic symptoms such as gastrointestinal discomfort, skin issues, migraines, or fatigue when no other clear cause is found.

Information overload
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Good
Harm:Elevated
Information overload is a state in which the amount of received stimuli and information exceeds the brain's processing capabilities. This phenomenon is intensifying in the digital age, leading to stress, fatigue, cognitive disturbances, and reduced quality of life. Excess digital content, doomscrolling, or constant access to social media exacerbate this problem, especially among young adults.

Insufficient protein intake
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
Too low protein intake is a serious risk factor for the deterioration of muscle and bone health, especially in the elderly and chronically ill. Chronic protein deficiency leads to weakness, loss of muscle mass, decreased physical performance, and accelerates the development of sarcopenia and osteoporosis. An adequate amount of dietary protein is essential for maintaining performance, regeneration, and metabolic health.

Insufficient veggie and fiber intake
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:Elevated
A deficiency of vegetables and fiber in the diet promotes the development of many chronic diseases, including cancers, intestinal disorders, and cardiovascular diseases. The lack of these nutrients leads to gut dysbiosis, chronic inflammation, and deterioration of metabolic parameters. Regularly including vegetables and fiber in the diet is essential for maintaining health and preventing disease.
Insulin & Metabolic Sensitivity
Level:Intermediate
Usefulness:High
This panel goes beyond basic glucose snapshots and helps identify early signs of insulin resistance — even in individuals with normal fasting glucose or HbA1c. It typically includes fasting insulin, HOMA-IR index, C-peptide, and sometimes OGTT (oral glucose tolerance test). Insulin resistance is a key driver of metabolic syndrome, weight gain, cardiovascular disease, and accelerated aging. Early detection allows for more proactive intervention — often through lifestyle changes alone.

Intense training before bed
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Good
Harm:Low
Intensive exercise performed at least 1–2 hours before sleep does not impair sleep quality in healthy adults, while also supporting recovery processes.

Intermittent fasting
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Low
Intermittent fasting (IF) is a dietary strategy that alternates periods of fasting with periods of eating. IF can support weight loss, improve lipid profiles, regulate glycemia, and reduce blood pressure. The greatest benefits are observed in individuals with overweight, obesity, and metabolic disorders.

Joint Range of Motion Assessment
Level:Beginner
Usefulness:High
This assessment evaluates the range of motion (ROM) in key joints such as the shoulders, elbows, hips, knees, and ankles. It helps detect limitations in flexibility, asymmetries between limbs, and potential movement dysfunctions. Measurements are taken using a goniometer to compare actual mobility to normative reference values, supporting injury prevention, rehabilitation, and athletic performance optimization. It is especially useful when designing a personalized training plan tailored to your movement capacities and limitations.

Lack of daylight exposure
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Good
Harm:Elevated
Lack of regular access to natural daylight disrupts the synchronization of the biological clock, leading to poorer sleep quality, mood disorders, and an increased risk of mental health problems. Limited contact with sunlight promotes delayed sleep phase and intensifies symptoms of depression and daytime sleepiness. These effects are observed both in the general population and among individuals with existing mood disorders.

Lack of life goals and motivation
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Good
Harm:Elevated
A lack of clearly defined goals and internal motivation promotes apathy, reduces psychological well-being, and impairs the body's adaptive responses to stress. It is accompanied by an increased risk of depression, weakened cardiovascular reactivity, and a higher incidence of cardiovascular diseases.

Lack of nature contact
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:Elevated
Lack of contact with nature is increasingly common in modern societies. Numerous studies show that limiting exposure to nature can have negative health effects, including on mental health, cognitive functions, and the immune system. People living in cities, deprived of regular contact with nature, are more prone to symptoms of stress, anxiety, depression, and also immune system weakness. Regular contact with nature, even on a small scale, brings significant health benefits, while its absence may lead to chronic health problems.

Lack of regular medical checkups
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Good
Harm:Elevated
Lack of regular medical check-ups increases the risk of late disease detection, leading to poorer treatment outcomes, especially in cases of heart disease, cancer, and metabolic syndrome. Regular preventive check-ups are crucial for early detection of diseases, which enables more effective treatment and reduces the risk of serious complications.

Light therapy masks
A practical guide to selecting a light therapy mask: wavelengths, irradiance, safety, coverage, and comfort — plus a comparison of popular models.
Lipid Panel
Level:Beginner
Usefulness:High
A lipid panel is a standard blood test used to evaluate the levels of fats in your blood, including total cholesterol, LDL, HDL, and triglycerides. These markers are key indicators of your risk for heart disease, stroke, and metabolic disorders. This test provides essential insights into how well your body is managing lipid transport, storage, and clearance — and how your lifestyle or diet may be influencing those processes.

Liver Function Panel
Level:Intermediate
Usefulness:Medium
The Liver Function Panel evaluates enzymes and proteins produced by the liver to assess its function and overall health. It includes markers like ALT, AST, GGT, ALP, bilirubin, and albumin. The liver is a central metabolic organ responsible for detoxification, nutrient processing, and hormone metabolism. Subtle dysfunction can impact energy levels, digestion, inflammation, and overall longevity — even in asymptomatic individuals.

Loneliness
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
Loneliness is a significant risk factor for many chronic diseases, including heart disease, stroke, depression, and dementia. Loneliness not only increases the risk of illness, but also worsens quality of life, leading to a decline in both mental and physical health. Studies show that loneliness is linked to chronic stress, emotional disorders, and impaired cognitive function, which affect both life span and quality. Interventions that reduce loneliness can improve health and contribute to better quality of life.
Low-intensity shockwave therapy (liswt)
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Low
Low-intensity shockwave therapy (LiSWT, ESWT) is a non-invasive method used in the treatment of erectile dysfunction and musculoskeletal disorders. The mechanism of action is based on stimulating regenerative processes, improving blood flow, and relieving pain. The most thoroughly studied efficacy is in the treatment of vascular-related erectile dysfunction and in selected tendinopathies and orthopedic conditions.

Magnesium
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Low
Magnesium is an essential mineral that supports proper cardiovascular function, brain health, and the musculoskeletal system. Adequate magnesium intake promotes blood pressure regulation, protection against arrhythmias, improved cognitive function, and the maintenance of muscle mass and strength. Supplementation is especially beneficial in individuals with deficiencies and increased risk of chronic diseases.

Magnetic Resonance Imaging (3T MRI)
Level:Beginner
Usefulness:High
Magnetic Resonance Imaging (MRI) is a non-invasive diagnostic technique that uses strong magnetic fields and radio waves to produce highly detailed images of the body’s internal structures. The 3 Tesla (3T) MRI offers significantly higher image resolution and faster scanning times compared to standard 1.5T devices. MRI is a cornerstone of modern diagnostics — essential for identifying tissue damage, inflammation, structural abnormalities, and early-stage diseases in the brain, spine, joints, and internal organs. It provides unmatched contrast for soft tissue visualization without exposing the patient to ionizing radiation. The 3T MRI is especially valuable for neurological, musculoskeletal, and cardiovascular imaging — supporting both preventive diagnostics and precise treatment planning.

Matcha
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Low
Matcha is powdered green tea rich in antioxidants, L-theanine, caffeine, and catechins. Regular consumption may support weight control, lipid profile, and insulin sensitivity, as well as reduce chronic inflammation. Studies also indicate moderate benefits for improving attention and cognitive function.

Meditation
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Negligible
Meditation is a practice involving conscious focus of attention, which shows multidimensional benefits for mental health, well-being, and cognitive performance. Numerous studies confirm that regular meditation reduces stress, anxiety, and depression, improves sleep quality, and supports cognitive abilities and emotional balance.

Metformin
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Low
Metformin is the first-line treatment for type 2 diabetes with a proven beneficial effect on glycemic control, body weight, and lipid profile. It acts in multiple ways, improving insulin sensitivity, supporting healthy metabolism, and reducing the risk of cardiovascular complications in individuals with diabetes and metabolic syndrome.

Methylene blue
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Preliminary
Risk:Elevated
Methylene Blue (MB) is a redox-active compound with unique properties that support mitochondrial efficiency, protect neurons, and modulate oxidative stress. Originally developed as a medical dye and antidote, it has gained attention in longevity science for its potential to enhance energy metabolism, protect against neurodegeneration, and promote cognitive health.
Micronutrient & Iron Panel
Level:Intermediate
Usefulness:Medium
This panel evaluates key micronutrient levels, including iron, ferritin, vitamin B12, folate, and others, to detect deficiencies or imbalances that may impact energy, cognition, immunity, or long-term health. While some nutrients are better tested via intracellular or functional markers, this blood-based panel offers a widely available and cost-effective screening option to guide dietary or supplemental interventions.

Microplastic Test
Level:Advanced
Usefulness:Medium
The PlasticTox Microplastics Screen (Arrow Lab Solutions) is an advanced laboratory analysis designed to detect and quantify microplastic particles circulating in human blood. Using specialized filtration and spectroscopic techniques, the test measures the number and size distribution of polymer particles to assess environmental exposure through food, water, air, and consumer products. Microplastics — typically defined as plastic fragments smaller than 5 mm — have been detected in human tissues, placenta, and bloodstream. Their presence raises concerns about potential inflammation, oxidative stress, and long-term toxic effects, though the biological impact remains under active scientific investigation. The PlasticTox screen provides an early insight into environmental toxic load and cumulative exposure. While it does not diagnose disease or toxicity, it offers valuable information for those interested in minimizing environmental pollutants and assessing potential bioaccumulation risk.
Mitochondrial Function Panel (Biovis)
Level:Advanced
Usefulness:Medium
The Mitochondrial Function Panel analyzes specific blood and urine markers associated with cellular energy production, oxidative stress, and mitochondrial resilience. Mitochondria are essential for ATP generation — the energy currency of all cells — and their dysfunction is linked to fatigue, aging, and chronic disease. This panel helps identify mitochondrial stress or damage that may be contributing to low energy, poor exercise tolerance, or cognitive fog, and guides further metabolic or nutritional interventions.
Molecular Genetic Microbiome Analysis (Biovis)
Level:Advanced
Usefulness:Medium
This test provides a detailed genetic profile of the gut microbiota using molecular biology methods. It identifies the presence and relative abundance of key bacterial strains, including beneficial, neutral, and potentially harmful microbes. The results may highlight dysbiosis, overgrowth of specific species (such as Candida or Clostridium), or underrepresentation of keystone taxa like Akkermansia or Faecalibacterium. Insights from this test can support targeted dietary, probiotic, and lifestyle interventions aimed at improving gut health, immune function, and systemic inflammation.

Morning exposure to artificial light (therapy lamp)
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Negligible
Morning exposure to high-intensity artificial light, especially enriched with blue spectrum (e.g., therapeutic lamps), supports circadian rhythm regulation and improves sleep efficiency and quality. This method is effective for both older adults and young adults, as well as individuals with sleep disorders, also enhancing subjective mood and alertness.

Morning exposure to natural light
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Negligible
Morning exposure to natural light positively influences sleep quality, mood, and circadian rhythm. Regular exposure to bright light during the first hours of the day helps individuals fall asleep faster, reduces the risk of depression, and improves overall well-being. Effects are confirmed in children, adults, the elderly, and clinical populations.

N-acetyl-l-cysteine (nac)
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Low
N-acetyl-L-cysteine (NAC) is a potent antioxidant with a broad spectrum of effects. It supports brain health by protecting neurons and reducing inflammation, improves semen parameters in men with reduced fertility, and protects the liver from toxic damage and oxidative stress. NAC supplementation is associated with improved cognitive function, semen quality, and liver biochemical parameters, provided that appropriate doses are used.

Neurocognitive Function Assessment (CNS Vital Signs)
Level:Intermediate
Usefulness:High
The CNS Vital Signs neurocognitive test is a clinically validated digital assessment tool that evaluates a wide range of brain functions. It includes multiple mini-tests (e.g., verbal memory, psychomotor speed, executive function) and generates a comprehensive cognitive performance profile. The results help identify cognitive strengths and weaknesses and can be tracked over time to detect subtle cognitive changes. It’s commonly used in clinical research, aging studies, and by practitioners interested in early signs of neurodegeneration or cognitive decline.

Nicotinamide riboside (nr)
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Low
Nicotinamide riboside (NR) is a precursor of NAD+, which plays a key role in cellular metabolism and neuroprotective functions. NR supplementation helps increase NAD+ levels in the body, which translates into potential benefits for liver health, energy metabolism, and brain function. It is well tolerated and safe for use, although the metabolic effects in humans require further clinical studies.

NMN
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Preliminary
Risk:Low
NMN (nicotinamide mononucleotide) is a natural precursor of NAD+, a key coenzyme in cellular energy processes. NMN supplementation may increase NAD+ levels, support glucose and lipid metabolism, improve insulin sensitivity, and promote neuronal protection and brain function. The strongest effects are observed in individuals with metabolic disorders and in aging models, while long-term effects and safety in humans require further research.

No daily routine
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Preliminary
Harm:Elevated
Irregularity in daily rhythm, especially regarding sleep, meals, and work, has a clearly negative impact on health. Disruptions of the circadian rhythm, irregular meals, and lack of fixed sleep hours are associated with a range of negative health effects, including increased risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, metabolic disorders, and mental health problems. Regularity in daily activities is crucial for maintaining optimal health.

No intellectual challenges
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Preliminary
Harm:Elevated
Lack of intellectual challenges and environmental stimulation can lead to severe deficits in cognitive, emotional, and social development, which has a significant impact on health and quality of life in later years. Especially in children and adolescents, brain development is highly dependent on intellectual stimuli and social interactions.

No screens before bedtime
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Negligible
Limiting screen use in the evening hours, especially in bed and just before sleep, is an effective and safe intervention that supports better sleep, concentration, and mental health. Studies show that even small changes in evening screen habits can bring measurable benefits for sleep, recovery, and overall well-being.

No uv filter
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
Not using sunscreens with UV protection significantly increases the risk of developing skin cancer because UV radiation is the main factor causing skin cancer. Regular use of UV filters is one of the most effective methods for preventing skin cancers, photoaging, sunburns, and DNA damage that can lead to mutations and cancer development. Sun protection is a key element of a healthy lifestyle and health prevention.

Noise
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
Environmental noise, especially from transportation and human activity, has a serious impact on both physical and mental health. Chronic exposure to noise increases the risk of developing many chronic diseases, such as cardiovascular diseases, hypertension, stroke, as well as mental health disorders, including depression and anxiety. Noise is one of the main risk factors affecting quality of life, causing both hearing loss and other health detriments. For this reason, it constitutes a significant public health threat that requires actions aimed at reducing noise exposure.

Nutritionally complete plant-based diet
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Low
A wholesome plant-based diet based on unprocessed plant foods provides numerous health benefits. It supports cardiovascular health, reduces the risk of various cancers, and improves metabolic control and lipid profiles. It is safe and effective when properly balanced, making it a valuable dietary intervention.

Omega-3 fatty acids
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Low
Omega-3 fatty acids, especially EPA and DHA, support brain health, improve cognitive function, relieve joint pain and inflammation, and have a beneficial effect on the cardiovascular system. Regular omega-3 supplementation is particularly recommended for older adults, individuals with joint disorders, and those at high cardiovascular risk.

OMICm Age (TruDiagnostic)
Level:Advanced
Usefulness:Low
The OMICm Age test by TruDiagnostic estimates an individual’s biological age using DNA methylation data derived from a blood sample. It compares the methylation status of specific CpG sites across the genome to large reference populations, generating an age prediction that reflects cumulative molecular and environmental influences on the body. This test represents the primary epigenetic clock used in the TruAge platform and serves as a benchmark for assessing the overall biological aging rate. It integrates genomic, lifestyle, and environmental factors to determine whether one’s biological age is younger or older than their chronological age. While it provides valuable insight into global aging processes, interpretation should be contextualized alongside other biomarkers such as DunedinPACE or physiological health metrics.

OMICm FitAge (TruDiagnostic)
Level:Advanced
Usefulness:Low
The OMICm FitAge test by TruDiagnostic provides an epigenetic estimate of functional fitness age, reflecting the body’s physiological capacity and cardiorespiratory health. It uses DNA methylation data to predict an equivalent “fitness age” that correlates with VO₂max, muscular efficiency, and overall metabolic performance. FitAge captures how lifestyle, training, and metabolic health influence biological resilience and performance capacity. A lower FitAge relative to chronological age indicates stronger aerobic conditioning and metabolic flexibility, while a higher FitAge may suggest deconditioning or systemic stress. Though primarily a research and optimization tool, OMICm FitAge offers valuable insight into how molecular-level regulation corresponds to physical performance and longevity potential.

Optimal bedroom temperature (15–19°c)
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Negligible
Maintaining a bedroom temperature between 20–25°C promotes deep and efficient sleep, reduces the number of awakenings, and enhances nighttime comfort. Both overheating and the sensation of cold can negatively impact sleep quality, so it is important to adjust the environment to individual needs.

Optimized macronutrient distribution (c40/f35/p25)
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Negligible
Optimizing macronutrient distribution in the diet—particularly by increasing protein and fiber intake and limiting saturated fats and simple sugars—contributes to improved metabolic parameters, body weight, and glycemic control. Effects depend on individual needs, health goals, and lifestyle, but benefits have been observed in both healthy individuals and those with metabolic disorders.

Overeating
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
Overeating is one of the main risk factors for chronic diseases such as obesity, cardiovascular diseases, diabetes, and mental disorders. Regular excess calorie intake leads to an increase in body fat, which worsens body composition and triggers metabolic changes that can lead to serious health consequences. Overeating, especially at night, intensifies these negative effects, contributing to increased risk of heart disease, hypertension, and atherosclerosis.

Painkiller and nsaid overuse
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Good
Harm:High
Abuse of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) and paracetamol leads to serious damage to the liver, kidneys, and intestines. Paracetamol overdose can cause liver cell damage, and long-term use of NSAIDs leads to hepatitis, impaired kidney function, damage to the intestinal barrier, and other health complications, especially in people with comorbidities.

Physical inactivity
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
Lack of physical activity has serious health consequences, including negative effects on the cardiovascular, musculoskeletal, and mental health systems. A long-term sedentary lifestyle promotes the development of heart disease, hypertension, diabetes, osteoporosis, and depression. Regular physical activity is an effective prevention for these diseases, improves quality of life, and increases the body’s overall fitness.

Plasmalogens
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Low
Plasmalogens are a unique group of membrane phospholipids naturally found in the human body, particularly abundant in the brain, heart, and immune system. Supplementation supports memory, cognitive function, cardiovascular health, and immunity, exhibiting anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties. Benefits have been observed in elderly individuals and in models of neurodegenerative and cardiometabolic diseases.

Prebiotics (inulin and galactooligosaccharides)
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Low
Prebiotics, such as inulin and galactooligosaccharides (GOS), support metabolic, immune, and gut health by modulating the gut microbiota, increasing the production of beneficial metabolites, and strengthening the gut barrier. Regular use may contribute to improved metabolic function, reduced inflammation, and enhanced immune resilience.

Probutyrate (butyric acid)
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Preliminary
Risk:Low
Butyric acid, a natural short-chain fatty acid, supports gut health, strengthens immunity, and may improve metabolic parameters. Supplementation with products such as ProButyrate may benefit individuals with disrupted microbiota or chronic inflammation.

Processed food
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
Ultra-processed food (UPF) refers to products that are highly industrially processed, containing numerous additives, sugars, saturated fats, and often low amounts of nutrients. Numerous epidemiological and clinical studies unequivocally indicate that regular consumption of large amounts of UPF leads to an increased risk of obesity, type 2 diabetes, cardiovascular diseases, worsening metabolic parameters, and mental health problems.

Proferrin (heme iron polypeptide)
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Low
Proferrin is a heme iron polypeptide with high bioavailability, intended for supplementation in individuals with iron deficiency. The supplement improves hemoglobin and ferritin levels, supporting the release and distribution of oxygen to tissues. Regular use of Proferrin can accelerate the replenishment of iron stores and increase physical performance.

Protein supplementation
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Negligible
Protein supplementation is widely used to increase lean body mass, improve recovery, and support proper metabolism, especially in older individuals, physically active people, and during weight reduction. The best effects are achieved when combined with resistance training or under caloric deficit. The effectiveness of supplementation depends on age, activity level, and health status.

Psychoactive substance abuse
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
The abuse of psychoactive substances – including alcohol, drugs, and medications used against recommendations – is one of the main causes of serious health problems worldwide. It leads to irreversible organ damage, cognitive impairment, mental disorders, and significantly reduces the quality and length of life of people affected by addiction.

Pure cocoa
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Negligible
Pure cocoa rich in flavonols and polyphenols has a beneficial effect on cardiovascular health, cognitive functions, and supports proper immune system function. Regular consumption of high-quality cocoa, without added sugar and fats, may help lower blood pressure, improve memory, attention, and neuroplasticity, and shows potential anti-inflammatory and immunomodulatory effects.
Rapamycin
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Preliminary
Risk:Elevated
Rapamycin, an mTOR pathway inhibitor, is being investigated as a potential agent to support healthy aging and cancer prevention. Its actions include modulation of cellular metabolism, enhancement of mitochondrial function, and inhibition of cancer cell proliferation, which may translate into delayed aging processes and disease progression. Despite promising results from preclinical studies, further validation in clinical trials is needed.

Red light therapy
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Negligible
Red light therapy is a non-invasive method that uses light with wavelengths between 600–700 nm to illuminate tissues, supporting the repair processes of skin, muscles, and bones. Its application in sports, dermatology, and orthopedics accelerates wound healing, reduces inflammation, and improves muscle strength and endurance. Numerous studies confirm its safety and effectiveness in humans.

Regular social contacts with close ones
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Negligible
Regular, high-quality social contact with close individuals contributes to maintaining mental sharpness, reducing stress levels, and improving psychological well-being. Long-term relationships and daily interactions support brain health by protecting against premature aging and the development of dementia. The benefits are particularly visible among older adults, but also present in younger age groups.
Renal Function Panel
Level:Intermediate
Usefulness:High
The Renal Function Panel is a group of blood tests used to assess how well your kidneys are filtering waste, balancing electrolytes, and maintaining internal homeostasis. It typically includes measurements of creatinine, blood urea nitrogen (BUN), estimated glomerular filtration rate (eGFR), and electrolytes such as sodium and potassium. This test is important for detecting early signs of kidney impairment, monitoring chronic kidney disease (CKD), and evaluating the impact of medications or systemic conditions on renal performance.
Resting Metabolic and Respiratory Analysis (PNOE)
Level:Beginner
Usefulness:High
The Resting Metabolic and Respiratory Analysis (PNOE) is a non-invasive test that evaluates your body’s metabolism through precise breath-by-breath gas analysis. It measures oxygen uptake (VO₂) and carbon dioxide output (VCO₂) to determine how efficiently your body converts nutrients into energy at rest. Using indirect calorimetry, the test calculates resting metabolic rate (RMR), fat versus carbohydrate utilization, and respiratory quotient (RQ). These values provide a detailed understanding of your metabolic flexibility, caloric needs, and overall energy balance — essential data for optimizing nutrition, training, and recovery strategies. PNOE technology is used worldwide by clinical, sports, and longevity professionals to personalize lifestyle programs based on individual metabolic profiles.

Restriction of blue light in the evening
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Negligible
Limiting exposure to blue light in the evening supports the natural circadian rhythm, facilitates falling asleep, and improves subjective sleep quality. This intervention is particularly beneficial for people with sleep problems, circadian rhythm disorders, and mental health conditions, as well as for shift workers or individuals exposed to artificial light in the evening.

Resveratrol
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Preliminary
Risk:Low
Resveratrol is a natural compound found in grapes, red wine, and certain berries, extensively studied for its potential benefits for heart and brain health. Laboratory and preclinical studies demonstrate its antioxidant, anti-inflammatory, endothelial-supporting, and neuroprotective effects. Preliminary clinical findings suggest possible beneficial effects on selected cardiovascular health markers and cognitive functions; however, the effectiveness of supplementation in humans has not been definitively confirmed.

Sauna
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Low
Sauna is a traditional health-supporting method that brings numerous benefits to the cardiovascular system, improves mental well-being, and aids in post-exercise recovery. Regular sauna use promotes lower blood pressure, improved vascular function, stress reduction, and better sleep quality, which collectively enhance quality of life and reduce the risk of chronic diseases.

Screen use before bed
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:Elevated
Using screens before sleep is a common phenomenon among children, adolescents, and adults. Research shows that exposure to light emitted by electronic devices in the evening negatively affects sleep duration and quality, leading to worsened brain functioning, concentration, and mental health. Limiting screen use before bedtime is an effective strategy to improve sleep and well-being.

Sedentary work
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
Sedentary work, characterized by prolonged sitting, is increasingly common in modern societies. Numerous scientific studies have shown that this work style is associated with an increased risk of cardiovascular diseases, mental disorders, and musculoskeletal complaints, leading to a deterioration of overall health and quality of life.
Semen Analysis
Level:Intermediate
Usefulness:Medium
Semen analysis — commonly used in fertility diagnostics — is increasingly recognized as a valuable tool for assessing a man's general health. It provides detailed insights into sperm concentration, motility, morphology, and total count, which can reflect hormonal status, metabolic function, oxidative stress, and even environmental toxin exposure. In the context of longevity, semen quality acts as a downstream product of the entire male organism. Poor results may point to chronic inflammation, endocrine disruption, mitochondrial dysfunction, or lifestyle imbalances — making it a useful biomarker beyond reproduction.

Serum Protein Electrophoresis
Level:Advanced
Usefulness:Low
Serum Protein Electrophoresis (SPEP) is a laboratory technique that separates proteins in the blood based on their size and electrical charge. It provides a visual distribution of protein fractions such as albumin, alpha, beta, and gamma globulins. The test is primarily used in clinical contexts to help diagnose and monitor disorders like multiple myeloma, monoclonal gammopathy of undetermined significance (MGUS), and chronic inflammatory or liver conditions. While not typically part of general health screening, it can offer insights when abnormal immune or protein metabolism is suspected.

Sex Hormones Panel
Level:Intermediate
Usefulness:High
The sex hormones panel measures critical regulators such as testosterone, estrogen, progesterone, and related markers. These hormones play major roles in energy levels, mood, sexual health, muscle mass, fertility, bone density, and even cognitive function. Testing is useful for identifying imbalances linked to aging, stress, overtraining, or metabolic dysfunction — and can help guide interventions like lifestyle changes, supplementation, or, in some cases, medical therapies.

Shift work
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Good
Harm:Elevated
Shift work, especially in rotating and night systems, leads to numerous health problems, both physical and mental. The pronounced impact of shift work is particularly noticeable in sleep disorders, chronic fatigue, depression, anxiety, and work-life balance disturbances. Shift workers, especially women and those with irregular shifts, are particularly vulnerable to these health effects.

Silence in the bedroom
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Negligible
Maintaining low noise levels in the bedroom significantly improves both objective and subjective sleep quality. Noise reduction promotes a longer duration of deep sleep (N3) and reduces sleep fragmentation, resulting in better well-being and less fatigue during the day. An optimal background noise level masks incidental sounds, minimizing micro-awakenings.
Skin Mole Mapping – Videodermatoscopy (Canfield D200 Evo)
Level:Intermediate
Usefulness:High
The Skin Mole Mapping examination uses videodermatoscopy — a high-resolution imaging technique that allows detailed visualization and documentation of pigmented skin lesions. Using the Canfield D200 Evo system, this test enables dermatologists to analyze the structure, color distribution, and symmetry of moles and identify early features suggesting atypia or malignant transformation. The examination is non-invasive, quick, and provides a digital baseline for long-term monitoring of existing lesions. It is an essential component of skin cancer prevention programs, especially for individuals with multiple moles, fair skin, or a family history of melanoma.

Sleep 7–9 hours per day
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Negligible
Sleeping 7–9 hours per night supports mental, cardiovascular, and cognitive health. Regular sleep within this range reduces the risk of mood disorders, heart disease, and declines in memory and concentration.

Sleep fragmentation
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
Sleep fragmentation, i.e. frequent awakenings at night, has a clearly negative effect on physical health, mental health, and cognitive functions. Even with similar total sleep duration, frequent awakenings lead to poorer sleep quality, greater fatigue, reduced cognitive performance, as well as metabolic and emotional disorders. Sleep fragmentation also increases the risk of neurodegenerative diseases such as Alzheimer's disease. Improving sleep continuity is crucial for health and longevity.

Sleep less than 7 hours
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
Sleep is essential for maintaining mental health, cardiovascular health, and cognitive function. Regular sleep of less than 7 hours a day increases the risk of developing depression, anxiety, memory and concentration problems, and also negatively affects the cardiovascular system, raising the risk of heart disease and mortality. Additionally, sleep restriction leads to deterioration in brain structure, reducing gray matter volume, which may promote neurodegenerative diseases.

Smoking tobacco
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
Smoking tobacco is one of the most thoroughly documented harmful health behaviors. It increases the risk of many chronic diseases, including cancers, cardiovascular diseases, chronic obstructive pulmonary disease (COPD), and many other health disorders. The scale of harm is enormous, and quitting smoking brings immediate health benefits, improving the functioning of many body systems.

Snacking
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Preliminary
Harm:Elevated
Snacking on unhealthy foods, especially those high in sugars, fats, and salt, has a negative effect on metabolism. Regular consumption of such snacks increases the risk of obesity, insulin resistance, lipid disorders, and metabolic syndrome, even if it does not lead to excessive calorie intake. Long-term snacking can also affect mental health, leading to depression, anxiety, and stress.

Spinach
Impact:High
Evidence:Strong
Spinach (Spinacia oleracea) is a nutrient-dense leafy green vegetable celebrated for its rich profile of vitamins, minerals, antioxidants, and bioactive compounds. It supports multiple aspects of health — from cellular protection and metabolic balance to cardiovascular and liver function. Regular consumption contributes to lower oxidative stress, improved lipid and glucose metabolism, and enhanced gut microbiota diversity. Due to its density of beneficial compounds and low caloric content, spinach is considered one of the most effective foods for maintaining vitality, preventing chronic disease, and supporting healthy aging.
Spirometry (ndd EasyOne Air)
Level:Intermediate
Usefulness:Medium
Spirometry (ndd EasyOne Air) is a non-invasive diagnostic test that measures how much air you can inhale and exhale and how quickly you can do so. It provides key insights into the condition of your lungs and the efficiency of your respiratory system, helping detect early signs of airway obstruction, restriction, or decreased pulmonary performance. The test evaluates fundamental respiratory parameters such as Forced Vital Capacity (FVC), Forced Expiratory Volume in one second (FEV₁), and Peak Expiratory Flow (PEF). These values indicate both the mechanical capacity of your lungs and the health of your airways. Regular spirometry is a cornerstone of preventive screening for respiratory conditions and overall cardiopulmonary health.
Stem cell therapy (msc)
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Preliminary
Risk:Elevated
Stem cell therapy is an innovative method aimed at supporting the body's repair and regenerative processes. Research suggests its potential efficacy in regenerating cartilage, bone, skin, liver, and nerves; however, clinical evidence remains limited, and its safety and long-term effects are not conclusively confirmed. The therapy is mainly used within clinical trials and is not a standard treatment for most conditions.

Strength/resistance training
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Low
Strength training is one of the most well-documented interventions supporting health, performance, and longevity. Regular resistance exercises lead to increased muscle mass and strength, improved bone mineral density, fat reduction, and enhanced joint stability. As such, strength training plays a key role in injury prevention, sarcopenia prevention, and maintaining functional fitness at every stage of life.

Sugary drinks
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Strong
Harm:High
Sweetened beverages, especially those sweetened with sugar, are one of the main risk factors for developing many chronic diseases such as obesity, type 2 diabetes, metabolic syndrome, and cardiovascular diseases. Regular consumption of these beverages has a clearly documented negative impact on health, contributing to an increased risk of death related to these conditions.

Sulforaphane
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Preliminary
Risk:Low
Sulforaphane is a natural isothiocyanate found in cruciferous vegetables, valued for its multi-directional health benefits. Preclinical and early clinical studies have demonstrated its neuroprotective action, support for gut barrier integrity, and ability to inhibit carcinogenesis. Regular intake of sulforaphane may aid in protecting against oxidative stress, inflammation, and proliferative pathologies.

SYMPHONY Age (TruDiagnostic)
Level:Advanced
Usefulness:Low
The SYMPHONY Age test by TruDiagnostic is an advanced epigenetic analysis that estimates biological aging across multiple organ systems. Using DNA methylation data, it models the biological age of 11 distinct physiological domains, including cardiovascular, immune, metabolic, neurological, and endocrine systems. This multi-system approach allows for a more granular understanding of how different parts of the body age relative to one another. For example, an individual may show a younger cardiovascular age but an older immune age, reflecting specific stressors or lifestyle influences. Although SYMPHONY Age provides rich contextual data, it is primarily a research and optimization tool rather than a diagnostic instrument. Interpretation requires understanding of systemic aging processes and integration with additional biomarkers.
Telomere Length (TruDiagnostic)
Level:Advanced
Usefulness:Low
The Telomere Length test by TruDiagnostic provides an indirect, epigenetic estimation of average telomere length using DNA methylation data. Unlike traditional telomere tests based on qPCR or HT-STELA methods, this approach predicts telomere length through machine learning models trained on methylation patterns correlated with chromosomal shortening. Telomeres are protective DNA-protein structures at the ends of chromosomes that shorten with each cell division, reflecting cumulative biological stress, oxidative damage, and cellular turnover. Shorter telomeres are associated with increased disease risk and aging-related decline. Although telomere biology is a central aging mechanism, methylation-based telomere estimates are currently less precise and carry limited individual diagnostic utility compared to other modern aging biomarkers.
Telomere Length Test (TeloNostiX)
Level:Advanced
Usefulness:Low
The Telomere Length Test (TeloNostiX) evaluates the average length of telomeres — the protective DNA sequences at the ends of chromosomes — using a high-precision method called High Throughput Single Telomere Length Analysis (HT-STELA). Telomeres naturally shorten as cells divide and age, and their length is influenced by genetics, lifestyle, and environmental factors. This test provides an estimate of biological aging at the cellular level by comparing your telomere length with population-based percentiles for your chronological age. Shorter telomeres are associated with accelerated cellular aging and increased risk for chronic diseases, while longer telomeres typically reflect better cellular maintenance and resilience. However, telomere dynamics are complex and may vary significantly between tissues and individuals.
Thyroid Panel
Level:Intermediate
Usefulness:High
The thyroid panel evaluates hormones that regulate metabolism, body temperature, energy production, and cognitive function. It typically includes TSH, Free T3, Free T4, and sometimes thyroid antibodies. Abnormal levels may lead to fatigue, weight fluctuations, mood changes, or increased cardiovascular risk. This test is especially relevant when symptoms of hypo- or hyperthyroidism are present — or as part of a routine metabolic and hormonal health evaluation within a longevity protocol.

Too intense training without recovery
Impact: Negative
Evidence:Good
Harm:Elevated
Intensive training without sufficient recovery can lead to serious health problems, including muscle tissue damage, increased risk of injury, and dysfunction of the musculoskeletal system. Lack of rest between training sessions can result in accumulating fatigue, decreased performance, and risk of overtraining.
Trucheck Intelli Multi-Cancer Screening (Datar Cancer Genetics)
Level:Beginner
Usefulness:High
Trucheck Intelli is a non-invasive blood-based cancer screening test developed by Datar Cancer Genetics (UK). It detects circulating tumor cells (CTCs) and tumor-associated markers in peripheral blood using advanced immunocytochemistry and molecular profiling. The goal is to identify the presence of malignancy before clinical symptoms appear. The test is designed for early detection of solid tumors across multiple organs (e.g., breast, prostate, colon, pancreas, lung, ovary) by isolating rare cells expressing cancer-associated proteins such as EpCAM and PanCK. It provides a binary result — “Detected” or “Not Detected” — indicating whether circulating tumor cells are present in the sample. While Trucheck Intelli represents an important advancement in non-invasive oncology diagnostics, its predictive value depends on tumor stage and cell shedding rate. A negative result does not guarantee absence of disease but suggests no circulating malignant cells were identified at the time of sampling.

Ubiquinol
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Negligible
Ubiquinol, the active and bioavailable form of coenzyme Q10, plays a key role in cellular energy production and protection against oxidative stress. Supplementation with ubiquinol may support cardiovascular function, improve physical performance, and promote cellular recovery in conditions of increased energy demand or metabolic stress.
Urinalysis
Level:Beginner
Usefulness:Medium
Urinalysis is a basic yet powerful diagnostic tool that analyzes the physical, chemical, and microscopic properties of urine. It helps evaluate hydration, detect urinary tract infections (UTIs), assess kidney function, and uncover signs of metabolic disorders such as diabetes. The test is fast, inexpensive, and often used in routine health screening or when symptoms like fatigue, frequent urination, or flank pain are present. It can detect early dysfunction before symptoms escalate.
Vitamin B
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Negligible
B vitamins play a key role in cellular metabolism, nervous system regeneration, and maintenance of proper brain function. Supplementation with B-complex supports energy processes, aids tissue repair, and may protect against cognitive impairment in individuals with deficiencies. The strongest effects are observed with vitamin B12 supplementation and when supplementing the entire B-complex in cases of increased demand or deficiency.

Vitamin D
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Low
Vitamin D is a key hormone involved in the regulation of immunity, neuron development and protection, and mood modulation. Maintaining adequate levels prevents deficiencies that lead to increased susceptibility to infections, autoimmune diseases, and neurodegenerative disorders. Vitamin D supplementation may also alleviate symptoms of depression and improve cognitive function in individuals with documented deficiency.
Vitamin K2
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Good
Risk:Negligible
Vitamin K2 supports bone mineralization, improves insulin sensitivity, and inhibits vascular calcification, translating into benefits for the musculoskeletal, metabolic, and cardiovascular systems. K2 supplementation may reduce fracture risk, improve glycemic control, and slow the progression of arterial calcification.
Vo2max
Impact:High
VO₂max measures the body’s ability to use oxygen during intense exercise — a direct marker of aerobic capacity, endurance, and metabolic efficiency. It is one of the most powerful indicators of healthspan and longevity.

Whoop Band
Level:Beginner
Usefulness:High
The Whoop Band is a continuous physiological monitoring device that measures heart rate variability (HRV), sleep quality, resting heart rate, strain, and recovery. Unlike fitness trackers focused on steps or calories, Whoop provides actionable insights into the body’s readiness, recovery status, and balance between stress and regeneration. Designed for athletes and longevity enthusiasts alike, Whoop helps users fine-tune training intensity, improve sleep, and manage stress levels — key foundations of long-term healthspan optimization. Its adaptive feedback loops make it one of the most useful tools for building self-awareness around lifestyle and performance patterns.
Young plasma transfusion
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Preliminary
Risk:Elevated
Young donor plasma transfusion is an innovative strategy being studied in the context of slowing aging processes, improving cognitive function, and positively influencing metabolism. Animal studies have shown memory improvement, neuron regeneration, and beneficial changes in health biomarkers, whereas clinical studies in humans have not confirmed significant therapeutic effects.

Zinc
Impact: Positive
Evidence:Strong
Risk:Low
Zinc is an essential trace element critical for the proper functioning of the immune system, regulation of glucose and lipid metabolism, and maintenance of healthy skin. Supplementation may enhance immune response, support glycemic and lipid control, accelerate wound healing, and reduce skin inflammation. Zinc is especially important for individuals with deficiencies, metabolic disorders, or chronic skin conditions.